读书笔记03《Redis设计与实现》
字典(哈希表)是一种非常常见的数据结构,也是Redis的核心数据结构。
在 Redis 中,每个数据库本身也是一个字典,而且字典也是 Redis 的 Hash 类型的底层实现。
Redis内部实现中采用了拉链法(seperate chaining)来解决冲突问题。
字典的数据结构
哈希表节点
哈希表节点用dictEntry结构来表示,每个dictEntry都保存一个键值对。
/*
* 哈希表节点
*/
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key; //键
// 值,三种类型
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
} v;
// 指向下个哈希表节点,形成拉链,解决冲突问题
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;
根据其结构可见, key 属性保存字典的键,而 v 属性则保存字典的值, next 保存一个指向 dictEntry 的指针,用于拉链法解决哈希值冲突问题。需要注意的是,v可以是一个指针,或者是一个uint64_t整数,或者是一个int64_t整数.
哈希表
哈希表结构由dictht定义,该结构体包含四个成员:
table是一个dictEntry指针数组,每个元素都指针一个dictEntry的指针,而每个dictEntry都保存着一个键值对。size记录哈希表的大小used记录已有节点的数量sizemaskmask码,用于地址索引的计算,其值等于size-1
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table;
unsigned long size;
unsigned long sizemask;
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
字典结构
dict结构定义如下:
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type; // 操作哈希表的一组函数,根据不同的值类型来定义
void *privdata; // 私有数据,传递给操作函数,可选参数
dictht ht[2]; // 配置两个哈希表
int rehashidx; // 指示 rehash 是否正在进行,如果不是则为 -1
int iterators; // 目前正在运行的iterator数量
} dict;
需要说明的是,每个字典使用两个哈希表,一般情况下只使用ht[0],当rehash时,使用ht[1],并且设置rehashidx索引。
令一方面,type属性指向了dictType指针,该结构定义了一组针对不同值类型的操作函数,实现了多态性。类似于nginx中针对不同的IO复用定了各自的事件函数,可见于ngx_event_actions_t结构体,dictType定义如下:
struct dictType {
// 计算哈希值的函数
unsigned int (*hashFunction)(const void *key);
// 复制键的函数
void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);
// 复制值的函数
void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);
// 对比键的函数
int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);
// 销毁键的函数
void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);
// 销毁值的函数
void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);
} dictType;</pre>
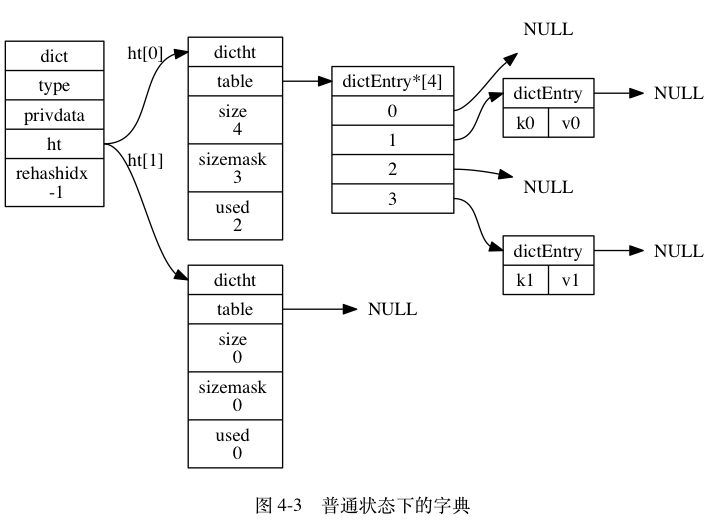
借个例子展示一个字典的内部结构(没有rehash)
图片来自:字典的实现
字典
哈希算法
添加新值到字典中时,首先要根据键来计算出哈希值和索引值,然后根据索引值来存储键值对。Reids内部采用的是MurmurHash2算法,MurmurHash2被很多软件采用,比如Memcached,Cassandra,HBase,Lucene等,也可以参考nginx中ngx_murmur_hash2对该算法的使用。
MurmurHash算法性能优越,自称每秒能hash 2056M的字符串数据。
Excellent performance - measured on an Intel Core 2 Duo @ 2.4 ghz
OneAtATime - 354.163715 mb/sec
FNV - 443.668038 mb/sec
SuperFastHash - 985.335173 mb/sec
lookup3 - 988.080652 mb/sec
MurmurHash 1.0 - 1363.293480 mb/sec
MurmurHash 2.0 - 2056.885653 mb/sec
unsigned int dictGenHashFunction(const void *key, int len) {
/* 'm' and 'r' are mixing constants generated offline.
They're not really 'magic', they just happen to work well. */
uint32_t seed = dict_hash_function_seed;
const uint32_t m = 0x5bd1e995;
const int r = 24;
/* Initialize the hash to a 'random' value */
uint32_t h = seed ^ len;
/* Mix 4 bytes at a time into the hash */
const unsigned char *data = (const unsigned char *)key;
while(len >= 4) {
uint32_t k = *(uint32_t*)data;
k *= m;
k ^= k >> r;
k *= m;
h *= m;
h ^= k;
data += 4;
len -= 4;
}
/* Handle the last few bytes of the input array */
switch(len) {
case 3: h ^= data[2] << 16;
case 2: h ^= data[1] << 8;
case 1: h ^= data[0]; h *= m;
};
/* Do a few final mixes of the hash to ensure the last few
* bytes are well-incorporated. */
h ^= h >> 13;
h *= m;
h ^= h >> 15;
return (unsigned int)h;
}
Redis将该哈希函数复制给一个dictType结构,用于dict的哈希值计算
static unsigned int _dictStringCopyHTHashFunction(const void *key)
{
return dictGenHashFunction(key, strlen(key));
}
dictType dictTypeHeapStringCopyKey = {
_dictStringCopyHTHashFunction, /* hash function */
_dictStringDup, /* key dup */
NULL, /* val dup */
_dictStringCopyHTKeyCompare, /* key compare */
_dictStringDestructor, /* key destructor */
NULL /* val destructor */
};
创建字典并初始化
Redis通过dictCreate来创建字段,申请到一个dict结构,然后调用_dictInit来初始化dict各项成员,在dictInit中调用了_dictReset初始化两个哈希表。
dict *dictCreate(dictType *type,
void *privDataPtr)
{
dict *d = zmalloc(sizeof(*d));//分配内存
_dictInit(d,type,privDataPtr);//调用dictInit初始化
return d;
}
int _dictInit(dict *d, dictType *type,
void *privDataPtr)
{
// 初始化两个哈希表的各项属性值
// 但暂时还不分配内存给哈希表数组
_dictReset(&d->ht[0]);
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
// 设置类型特定函数
d->type = type;
// 设置私有数据
d->privdata = privDataPtr;
// 设置哈希表 rehash 状态
d->rehashidx = -1;
// 设置字典的安全迭代器数量
d->iterators = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
static void _dictReset(dictht *ht)
{
ht->table = NULL;
ht->size = 0;
ht->sizemask = 0;
ht->used = 0;
}
刚创建字典时,ht[0]和ht[1]都为空,当通过dictAdd加入元素时,开始为ht[0]分配空间,在dictAdd中会调用dictAddRaw来实现,其中通过_dictKeyIndex来计算索引值。
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key)
{
int index;
dictEntry *entry;
dictht *ht;
// 如果条件允许的话,进行单步 rehash
// T = O(1)
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
/* Get the index of the new element, or -1 if
* the element already exists. */
// 计算键在哈希表中的索引值
// 如果值为 -1 ,那么表示键已经存在
// T = O(N)
if ((index = _dictKeyIndex(d, key)) == -1)
return NULL;
// T = O(1)
/* Allocate the memory and store the new entry */
// 如果字典正在 rehash ,那么将新键添加到 1 号哈希表
// 否则,将新键添加到 0 号哈希表
ht = dictIsRehashing(d) ? &d->ht[1] : &d->ht[0];
// 为新节点分配空间
entry = zmalloc(sizeof(*entry));
// 将新节点插入到链表表头
entry->next = ht->table[index];
ht->table[index] = entry;
// 更新哈希表已使用节点数量
ht->used++;
/* Set the hash entry fields. */
// 设置新节点的键
// T = O(1)
dictSetKey(d, entry, key);
return entry;
}
字典拓展
随着对字典的不断操作,其负载可能越来越大,为了维持负载因子在一个合理范围,需要对哈希表进行扩展或者收缩,这个过程称为rehash.
rehash过程可以描述为:
- 为字典的1号哈希表分配空间,新空间至少为已使用节点的两倍。
- 将保存到0号哈希表的键值,重新计算哈希值和索引值,并保存到1号哈希表中。
- 将0号键值对都迁移到1号哈希表上后,释放0号空间,将ht[1]置为ht[0],并为ht[1]新建一个空白哈希表。
每次添加元素都会通过_dictExpandIfNeeded函数来判断是否进行拓展.
static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d)
{
// 一下两个条件之一为真时,对字典进行扩展
// 1)字典已使用节点数和字典大小之间的比率接近 1:1
// 并且 dict_can_resize 为真
// 2)已使用节点数和字典大小之间的比率超过 dict_force_resize_ratio
if (d->ht[0].used >= d->ht[0].size &&
(dict_can_resize ||
d->ht[0].used/d->ht[0].size > dict_force_resize_ratio))
{
return dictExpand(d, ((d->ht[0].size > d->ht[0].used) ?
d->ht[0].size : d->ht[0].used)*2);
}
......
}
具体的扩容操作由dictExpand函数来进行,该函数的作用就是:创建一个新的哈希表,打开字典的rehash标识,使得程序可以进行rehash。
渐进式rehash
在上面的dictExpand中,其打开了字典的rehash标识,标识打开后redis就行进行rehash过程,值得注意的是,这个rehash的过程并不是一次性完成,因为如果字典中有大量键值对的话,一次性完成将会影响redis服务器的性能。在Redis中,这个过程被平摊到dictAddRaw 、 dictGetRandomKey 、 dictFind 和 dictGenericDelete 这四个函数里面,每次调用他们都会执行_dictRehashStep操作,直到rehash完成。
整个渐进式的rehash过程的状态,是通过字典的rehashidx来记录的,每个一次迁移,则rehashidx增1,当0号哈希表为空时,rehashidx=-1,标识rehash完成。
//执行 N 步渐进式 rehash 。
//返回 1 表示仍有键需要从 0 号哈希表移动到 1 号哈希表,
//返回 0 则表示所有键都已经迁移完毕。
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
// 只可以在 rehash 进行中时执行
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;
// 进行 N 步迁移
// T = O(N)
while(n--) {
dictEntry *de, *nextde;
/* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */
// 如果 0 号哈希表为空,那么表示 rehash 执行完毕
// T = O(1)
if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {
// 释放 0 号哈希表
zfree(d->ht[0].table);
// 将原来的 1 号哈希表设置为新的 0 号哈希表
d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];
// 重置旧的 1 号哈希表
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
// 关闭 rehash 标识
d->rehashidx = -1;
// 返回 0 ,向调用者表示 rehash 已经完成
return 0;
}
/* Note that rehashidx can't overflow as we are sure there are more
* elements because ht[0].used != 0 */
// 确保 rehashidx 没有越界
assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned)d->rehashidx);
// 略过数组中为空的索引,找到下一个非空索引
while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) d->rehashidx++;
// 指向该索引的链表表头节点
de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx];
/* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */
// 将链表中的所有节点迁移到新哈希表
while(de) {
unsigned int h;
// 保存下个节点的指针
nextde = de->next;
/* Get the index in the new hash table */
// 计算新哈希表的哈希值,以及节点插入的索引位置
h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask;
// 插入节点到新哈希表
de->next = d->ht[1].table[h];
d->ht[1].table[h] = de;
// 更新计数器
d->ht[0].used--;
d->ht[1].used++;
// 继续处理下个节点
de = nextde;
}
// 将刚迁移完的哈希表索引的指针设为空
d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;
// 更新 rehash 索引
d->rehashidx++;
}
return 1;
}
渐进式rehash期间的哈希表操作
在rehash期间,如果执行字典的查询、更新、删除都会现在0号表中操作,如果没有则在1号表中操作;如果执行添加操作,则一律在1号表中添加。
字典API
最后列出Redis字典操作的API
| api | 作用 | 时间辅助度 |
|---|---|---|
dictCreate |
创建一个新的字典 | O(1) |
dictAdd |
添加键值对 | O(1) |
dictReplace |
更新键值对 | O(1) |
dictFetchValue |
获取给定键的值 | O(1) |
dictGetRandomKey |
返回一个随机键值对 | O(1) |
dictDelete |
删除给定键值对 | O(1) |
dictRelease |
释放字典及所有键值对 | O(N) |
dictScan |
迭代给定字典中的所有元素 | O(N) ? |
前面介绍了dictCreate和dictAdd的流程,就跳过了。
dictReplace替换
dictReplace的流程为:内部先通过dictAdd来尝试添加键值对到字典,如果添加成功dictAdd会返回DICT_OK,否则代表该键已经存在,此时则直接通过dictSetVal来设置键对应的新的值,通过释放旧值。
/*
* 如果键值对为全新添加,那么返回 1 。
* 如果键值对是通过对原有的键值对更新得来的,那么返回 0 。
*
* T = O(N)
*/
int dictReplace(dict *d, void *key, void *val)
{
dictEntry *entry, auxentry;
/* Try to add the element. If the key
* does not exists dictAdd will suceed. */
// 尝试直接将键值对添加到字典
// 如果键 key 不存在的话,添加会成功
// T = O(N)
if (dictAdd(d, key, val) == DICT_OK)
return 1;
/* It already exists, get the entry */
// 运行到这里,说明键 key 已经存在,那么找出包含这个 key 的节点
// T = O(1)
entry = dictFind(d, key);
/* Set the new value and free the old one. Note that it is important
* to do that in this order, as the value may just be exactly the same
* as the previous one. In this context, think to reference counting,
* you want to increment (set), and then decrement (free), and not the
* reverse. */
// 先保存原有的值的指针
auxentry = *entry;
// 然后设置新的值
// T = O(1)
dictSetVal(d, entry, val);
// 然后释放旧值
// T = O(1)
dictFreeVal(d, &auxentry);
return 0;
}
dictFetchValue查找
对Redis字典的查询过程很简单,先计算哈希值、索引值,然后在dict的两个哈希表中对应的索引位置进行比较即可。
dictEntry *dictFind(dict *d, const void *key)
{
dictEntry *he;
unsigned int h, idx, table;
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return NULL; /* We don't have a table at all */
// 渐进式rehash的平摊操作
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
// 计算键的哈希值
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
// 在字典的0号和1号哈希表中查找这个键
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
// 计算索引值
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
// 遍历给定索引上的链表的所有节点,查找 key
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
while(he) {
//比较键是否相同,相同就返回
if (dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key))
return he;
he = he->next;
}
// 如果程序遍历完 0 号哈希表,仍然没找到指定的键的节点
// 那么程序会检查字典是否在进行 rehash ,如果没有进行rehash,则可以直接返回NULL
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return NULL;
}
// 进行到这里时,说明两个哈希表都没找到
return NULL;
}
dictFetchValue通过dictFind获取到节点后,就可以返回键对应的值了。
void *dictFetchValue(dict *d, const void *key) {
dictEntry *he;
he = dictFind(d,key);//查找键对应的节点
return he ? dictGetVal(he) : NULL;
}
删除给定键
删除给定键过程:可能需要先rehash,然后计算哈希值,遍历两个哈希表,计算索引值,找到节点,从链表中删除,释放节点空间。
static int dictGenericDelete(dict *d, const void *key, int nofree)
{
unsigned int h, idx;
dictEntry *he, *prevHe;
int table;
// 字典(的哈希表)为空
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return DICT_ERR; /* d->ht[0].table is NULL */
// 进行单步 rehash ,T = O(1)
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
// 计算哈希值
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
// 遍历哈希表
// T = O(1)
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
// 计算索引值
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
// 指向该索引上的链表
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
prevHe = NULL;
// 遍历链表上的所有节点
// T = O(1)
while(he) {
if (dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)) {
// 超找目标节点
/* Unlink the element from the list */
// 从链表中删除
if (prevHe)
prevHe->next = he->next;
else
d->ht[table].table[idx] = he->next;
// 释放调用键和值的释放函数?
if (!nofree) {
dictFreeKey(d, he);
dictFreeVal(d, he);
}
// 释放节点本身
zfree(he);
// 更新已使用节点数量
d->ht[table].used--;
// 返回已找到信号
return DICT_OK;
}
prevHe = he;
he = he->next;
}
// 如果执行到这里,说明在 0 号哈希表中找不到给定键
// 那么根据字典是否正在进行 rehash ,决定要不要查找 1 号哈希表
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break;
}
// 没找到
return DICT_ERR; /* not found */
}
dictGetRandomKey返回一个随机键值对
dictGetRandomKey函数的执行流程为:可能先执行rehash,选择0号或者1号表作为随机的哈希表对象,计算出随机一个索引值,再从该索引值对应的链表中随机一个节点,返回随机节点。
Note:该过程用到了random()
dictRelease释放字典
dictRelease通过调用dictClear来循环清空两个哈希表,然后再释放dict结构空间。
void dictRelease(dict *d)
{
// 删除并清空两个哈希表
_dictClear(d,&d->ht[0],NULL);
_dictClear(d,&d->ht[1],NULL);
// 释放节点结构
zfree(d);
}
dictClear函数内部遍历哈希表上所有桶,对桶上的节点链表循环删除、释放节点,最后重置哈希表属性。
dictScan迭代字典中所有元素
目前还没搞懂…
Note
Redis源码的注释均参考自 huangz1990/redis-3.0-annotated
Reference
- 黄健宏. Redis设计与实现[M]. 机械工业出版社, 2014.
- MurmurHash
- redis-dict-implement.md